Java - 代理模式
Java 代理模式解析
一、代理模式
1、定义
代理模式是一种结构性模式。
代理模式给某个对象(用户)提供一个代理对象,通过代理对象来控制对原对象的访问,并允许在将请求交给对象前后进行一些处理。
用户通过中介租房的整个流程就是一个标准的代理模式。
2、三要素
- 服务接口:是一个接口,其中声明了服务。代理类只有实现了此接口才能伪装成服务对象。
- 服务:是一个类,它实现了服务接口,用于为用户提供服务。
- 代理:是一个类,它需要实现服务接口,是对服务类的包装。
在租房流程中:出租房屋这个动作是服务接口;房东可以看作是服务类,房东出租房屋就是服务类实现了服务接口;中介即代理类。
3、分类
根据代理的加载时机,代理模式可分为静态代理(Static Proxy)和动态代理(Dynamic Proxy)。
- 静态代理:代理类由程序员自己实现好,程序运行前就已生成了代理类的.class文件。
- 动态代理:代理类由反射机制动态生成,在程序运行时动态生成类字节码并加载到JVM中。
二、静态代理
普通模式与指定代理的区别是:前者可以自由使用任意实现了服务接口的代理类;而后者只能由服务类来指定代理类。
1、普通模式
A.定义
public interface Rent { //租房服务接口
void rentHouse();
}
public class NormalRentService implements Rent { //出租普通房屋的服务类
@Override
public void rentHouse() {
System.out.println("Rent a normal house to user...");
}
}
public class VillaRentService implements Rent { //出租别墅的服务类
@Override
public void rentHouse() {
System.out.println("Rent a villa to user...");
}
}
public class RentProxy implements Rent{ //代理类
private Rent rent; //被代理类(服务类)
public RentProxy(Rent rent) { //利用构造方法传入被代理的类
this.rent = rent;
}
@Override
public void rentHouse() { //代理类实现服务接口中的方法
System.out.println("I'm a rent proxy,i am looking for a suitable house for user...");
rent.rentHouse(); //调用服务类的出租方法(调用真实的出租方法)
System.out.println("Rent successfully,i earned one billion...");
}
}
B.使用
class RentProxyTest {
@Test
void normalRentTest() {
RentProxy proxy = new RentProxy(new NormalRentService()); //用NormalRentService类创建代理类
proxy.rentHouse(); //调用代理类的出租方法
}
@Test
void villaRentTest() {
RentProxy proxy = new RentProxy(new VillaRentService()); //用VillaRentService类创建代理类
proxy.rentHouse(); //调用代理类的出租方法
}
}
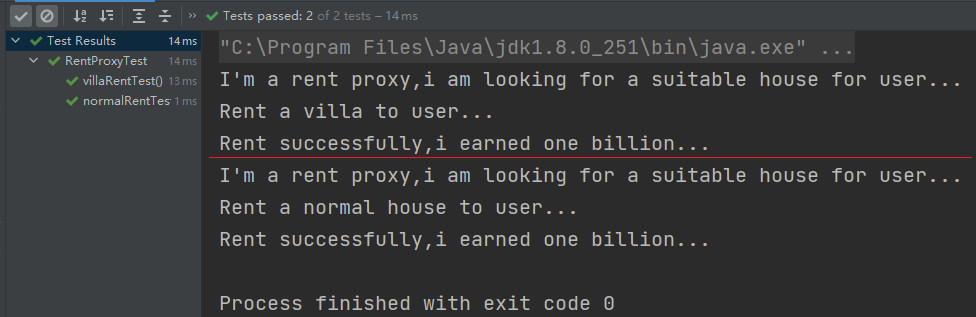
运行结果:
2、指定代理
A.定义
public interface Rent {
void rentHouse();
Rent getProxy(); //接口中新增此方法,用于指定代理类
}
public class NormalRentService implements Rent {
@Override
public void rentHouse() {
System.out.println("Rent a normal house to user...");
}
@Override
public Rent getProxy() {
return new RentProxy(this); //指定代理类为RentProxy
}
}
public class VillaRentService implements Rent {
@Override
public void rentHouse() {
System.out.println("Rent a villa to user...");
}
@Override
public Rent getProxy() {
return new AnotherRentProxy(this); //指定代理类为AnotherRentProxy
}
}
public class RentProxy implements Rent{ //AnotherRentProxy类与RentProxy类相似,此处省略其定义代码
private Rent rent;
public RentProxy(Rent rent) {
this.rent = rent;
}
@Override
public void rentHouse() {
System.out.println("I'm a rent proxy,i am looking for a suitable house for user...");
rent.rentHouse();
System.out.println("Rent successfully,i earned one billion...");
}
}
B.使用
class RentProxyTest {
@Test
void normalRentTest() {
RentProxy proxy = (RentProxy) new NormalRentService().getProxy(); //获取指定的代理类
proxy.rentHouse();
}
@Test
void villaRentTest() {
AnotherRentProxy proxy = (AnotherRentProxy) new NormalRentService().getProxy(); //获取指定的代理类
proxy.rentHouse();
}
}
运行结果:省略,与普通模式相同。