SpringBoot - AOP使用手册
SpringBoot中AOP使用教程
一、AOP
1.AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming,面向切面编程),是对OOP(Object Oriented Programming,面向对象编程)的一种补充;
2.OOP的关键是类(Class),侧重于对象的封装、继承;AOP的关键是切面(Aspect),侧重于对业务代码中某一公共行为的提取;
3.AOP可以在不修改业务代码的情况下,在连接点(Join point)向现有代码中添加一些自定义行为(Advice);
4.SpringBoot中AOP的底层原理是动态代理技术,AOP的主要应用场景是事务管理、日志记录、用户权限校验等;
二、术语
以下英文摘自官网,中文为个人理解。
1.连接点 (Join point)
A point during the execution of a program, such as the execution of a method or the handling of an exception. In Spring AOP, a join point
always represents a method execution.
切面与逻辑代码的连接点,在SpringBoot中的连接点是方法的执行。
2.切点 (Pointcut)
A predicate that matches join points. Advice is associated with a pointcut expression and runs at any join point matched by the pointcut
(for example, the execution of a method with a certain name). The concept of join points as matched by pointcut expressions is central
to AOP, and Spring uses the AspectJ pointcut expression language by default.
切点是用来匹配连接点的谓语表达式,AOP根据切点匹配到在哪些连接点上执行Advice。
切点与连接点的关系就像正则表达式与符合正则表达式的值的关系,二者是两个不同维度的东西。
不难看出 Pointcut 是 AOP 的核心。
3.通知 (Advice)
Advice在有的文章中翻译成增强,有的文章中又翻译为通知,本文中统一翻译为通知。
了解其作用即可,不必纠结于翻译结果。就像马铃薯在新疆称为洋芋,在广东叫土豆,实际都是同一个东西。
Action taken by an aspect at a particular join point. Different types of advice include "around," "before" and "after" advice. Many AOP
frameworks, including Spring, model an advice as an interceptor, maintaining a chain of interceptors around the join point.
AOP在连接点处具体执行的操作。
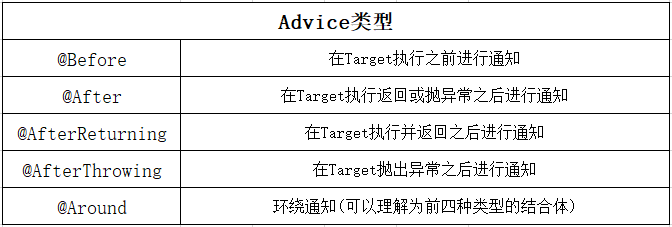
SpringBoot中通知执行的时间点有五个:@Before、@After、@AfterReturning、@AfterThrowing、@Around,下文详细介绍。
4.切面 (Aspect)
A modularization of a concern that cuts across multiple classes. Transaction management is a good example of a crosscutting concern in
J2EE applications. In Spring AOP, aspects are implemented using regular classes (the schema-based approach) or regular classes annotated
with the @Aspect annotation (the @AspectJ style).
切点和通知构成一个切面。
在SpringBoot中切面通常是一个@Aspect注解标注的类。
5.目标 (Target)
Object being advised by one or more aspects. Also referred to as the advised object. Since Spring AOP is implemented using runtime proxies
, this object will always be a proxied object.
被通知的对象。
6.织入 (Weaving)
Linking aspects with other application types or objects to create an advised object. This can be done at compile time (using the AspectJ
compiler, for example), load time, or at runtime. Spring AOP, like other pure Java AOP frameworks, performs weaving at runtime.
将切面和业务逻辑连接,并创建代理对象的过程叫织入。在SpringBoot中,织入是发生在代码运行期间。
7.引入 (Introduction)
Declaring additional methods or fields on behalf of a type. Spring AOP allows you to introduce new interfaces (and a corresponding
implementation) to any advised object. For example, you could use an introduction to make a bean implement an IsModified interface, to
simplify caching. (An introduction is known as an inter-type declaration in the AspectJ community.)
在不修改类的情况下,为该类引入一个新的接口,意味着可以执行该类中不存在的方法。
8.AOP代理 (AOP proxy)
An object created by the AOP framework in order to implement the aspect contracts (advise method executions and so on). In the Spring
Framework, an AOP proxy will be a JDK dynamic proxy or a CGLIB proxy.
AOP框架创建的一个代理对象,这个代理对象负责执行通知和目标对象的连接点方法。
三、理解
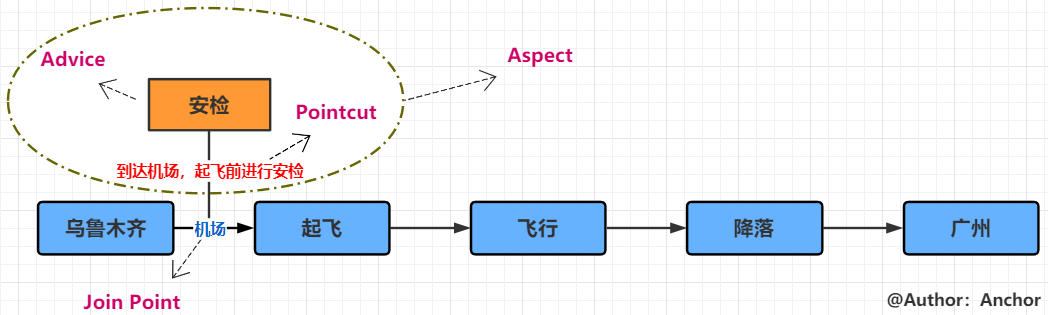
以乘客坐飞机从乌鲁木齐到广州为例(或参考此文):
1.正常处理逻辑是,乘客从乌鲁木齐某地点出发、起飞、飞行、降落、到达广州某一地点;
2.在乌市某地出发和起飞这两流程之间插入一个安检动作,此时安检就是AOP中的通知(Advice);
3.安检发生在机场,则机场就是连接点(Join point);对安检时间做一个限定:到达机场且飞机起飞前,这个限定条件就是切点(Pointcut);
4.其余上文中列出的术语在实际应用中很少用到;
四、解析
1.@Pointcut
1)SpringBoot中通过注解@Pointcut(“xxx”)来定义一个Pointcut,xxx用来匹配连接点。
2)xxx中可以使用以下10个关键字,最常用的是execution和@annotation,其余了解即可(可参考此篇文章)。
3)10个关键字之间可以通过 &&、||、! 组合使用,分别代表与、或、非。例:execution(XXX) && @annotation(xxx)
PS:建议将项目中所有Pointcut定义在一个类中,在切面类中通过完整类名 + 方法名使用。

4)execution
/**
* execution(public * anchor.mybatis.controller.CommonController.aopTest(..)) 解析:
*
* public —— 方法修饰符,可省略,省略时默认为 public
* * —— 方法返回值,* 代表任意类型返回值
* anchor.mybatis.controller —— 包名
* CommonController —— 类名
* aopTest —— 方法名
* .. —— 方法入参,‘..’ 代表任意个数、任意类型的参数
*/
public class CommonPointcut {
@Pointcut("execution(public * anchor.mybatis.controller.CommonController.aopTest(..))") //连接点是aopTest()方法
public void executionExp() {}
}
几个execution写法的例子:
A.execution(public * *(..))
含义:匹配任意返回值、任意包任意类中、任意方法名、任意个数和类型的public方法
B.execution(String anchor.mybatis..*(*,String))
含义:匹配 anchor.mybatis 包及其子包下所有返回值为String、有两个入参(第一个任意类型,第二个为String类型)的方法
C.execution(anchor.common.response.BaseResponse anchor.mybatis..get*(*))
含义:匹配 anchor.mybatis 包及其子包下所有返回值为BaseResponse类、只有一个入参且入参类型不限、方法名以get开头的方法
PS:AOP只能作用于Public和有限条件下的Protected的方法。Why?补充下基础知识…
5)@annotation
public class CommonPointcut {
@Pointcut("@annotation(anchor.mybatis.aop.LogTag)") //@annotation()表明将 注解@LogTag 标注的方法作为连接点
//@Pointcut("@annotation(LogTag)") CommonPointcut类 与 @LogTag注解 在同一包下时,可以只写注解名
private void annotationExp() {}
}
2.Advice
@Aspect //使用@Aspect注解来定义一个切面
@Component
public class LogAdvice {
@Before("CommonPointcut.executionExp1()") //使用同一个包下定义的Pointcut
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) { //JoinPoint用于获取连接点的信息,
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); //获取方法入参
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); //获取方法签名(返回值、方法名称)
String staticPart = joinPoint.getStaticPart().toLongString(); //获取方法相关的静态对象
}
@Around(value = "CommonPointcut.executionExp1()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { //ProceedingJoinPoint是JoinPoint的子类,只是多了执行功能
Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed(); //ProceedingJoinPoint只能用于@Around
return proceed;
}
}
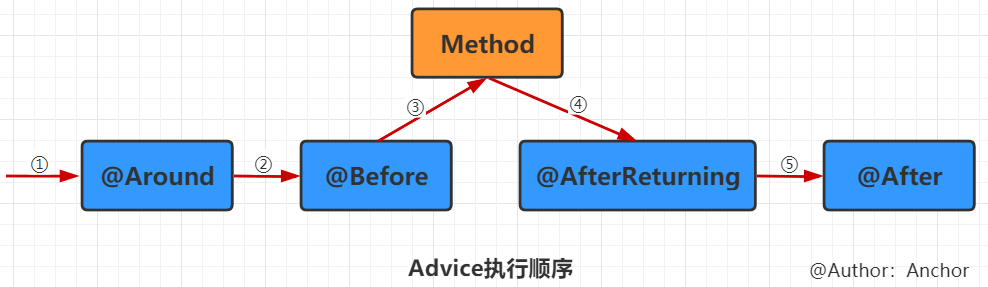
1)Advice一般都使用@Around,因为它最强大,其他四个Advice能实现的它都能做。
2)proceed()方法可以控制连接点什么时候执行,在proceed()之前可以实现@Before、之后可以做相应的@After操作。
五、使用
1.引入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
<version>${latestVersion}</version>
</dependency>
PS:在IDEA中使用AOP时可以打开下面这个插件,体验较好。
2.实例
package anchor.mybatis.aop;
public class CommonPointcut { //定义Pointcut
@Pointcut("execution(* anchor.mybatis.controller.CommonController.aopTest(..))")
public void executionExp1() {
}
}
package anchor.mybatis.aop;
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAdvice { //使用@Aspect注解定义切面
@Before("CommonPointcut.executionExp1()")
public void before() {
log.info("Before advice...");
}
@After("execution(* anchor.mybatis.controller.CommonController.aopTest(..))") //也可以直接在Advice中定义Pointcut
public void after() {
log.info("After advice...");
}
@AfterReturning(value = "CommonPointcut.executionExp1()", returning = "result") //接收连接点的返回值
public void afterReturning(Object result) {
log.info("AfterReturning advice, return value is {}...", result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "CommonPointcut.executionExp1()", throwing = "exception") //接收抛出的异常
public void afterReturning(Exception exception) {
log.info("AfterThrowing advice, exception is {}...", exception.toString());
}
@Around(value = "CommonPointcut.executionExp1()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
log.info("Entering around advice...");
try {
return joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
log.info("Around catch an exception,exception is {}...", throwable.toString());
throw throwable;
}finally {
log.info("Exiting around advice...");
}
}
}
package anchor.mybatis.controller;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/common")
public class CommonController {
@Resource
private CommonService commonService;
@GetMapping("/aopTest")
public BaseResponse<Boolean> aopTest(String aa, String bb){
return new BaseResponse<>(commonService.aopTest());
}
}
package anchor.mybatis.service.impl;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class CommonServiceImpl implements CommonService {
@Override
public boolean aopTest() { //连接点
log.info("Executing aopTest()");
return true;
}
}
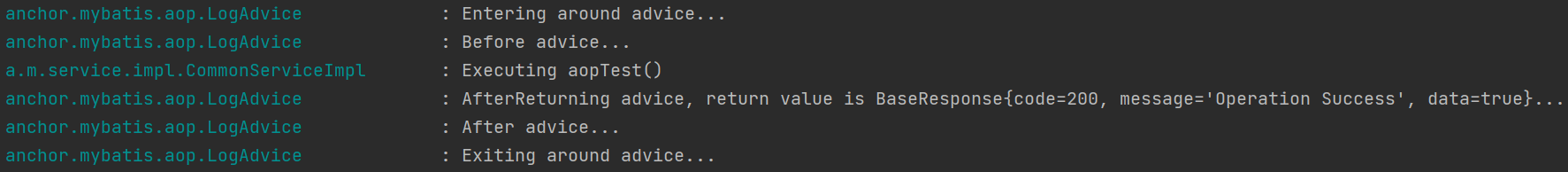
运行结果:
六、总结
1.AOP的核心概念是:Pointcut、PCD(PointCut Designators)、Advice。
2.AOP在SpringBoot中是:@Aspect + @Pointcut + @Around(或其他)。
3.AOP是Spring的三大支柱之一(IOC、DI、AOP),功能很强大,但是它实际上是一种不同于OOP的编程思想。