SpringBoot - 默认异常处理机制探索
SpringBoot默认异常处理机制探索
前言
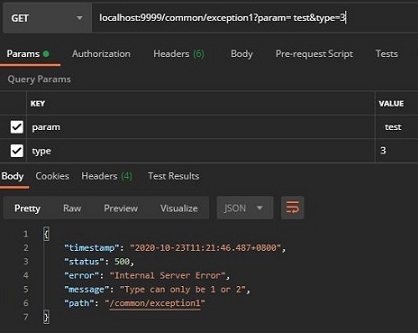
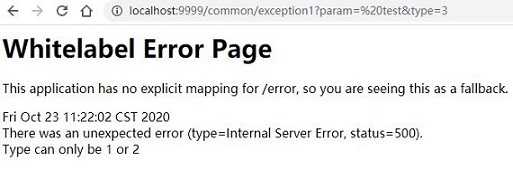
使用 Postman 和浏览器访问 SpringBoot 的接口异常时默认会返回如下信息,本文着重于探索异常抛出到返回下图中信息的整个过程。
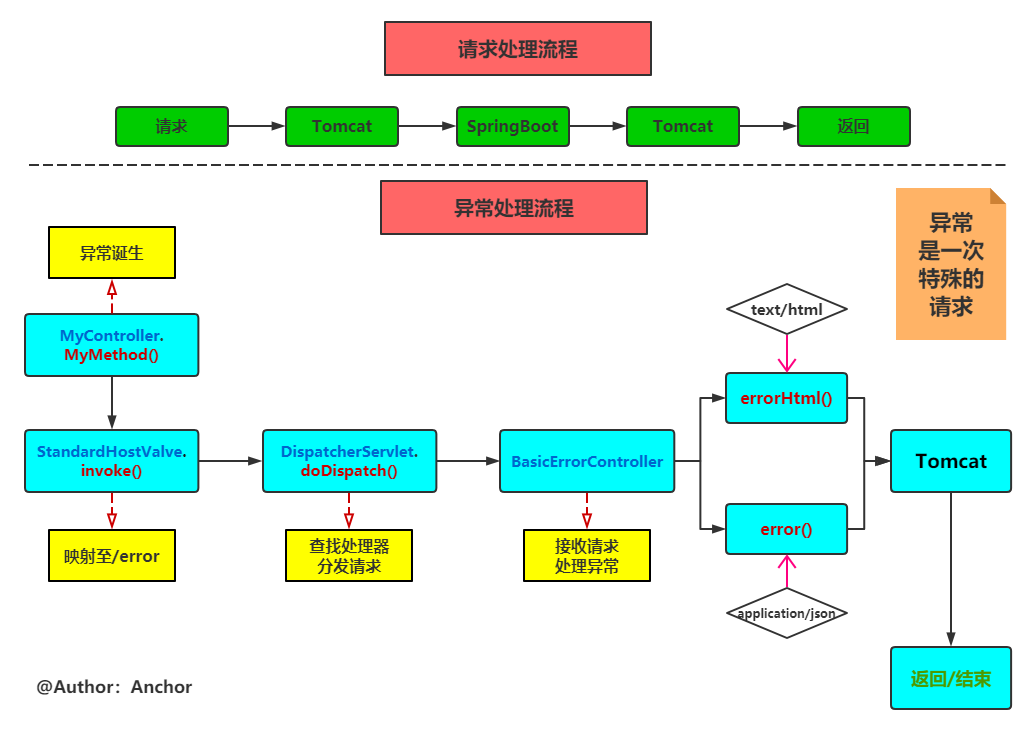
注:异常处理过程实质上是一次特殊的请求处理过程。
流程
自动配置
1)自动配置类ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration中配置了一些组装错误信息页所需要的组件(Bean);
2)最后一个注解注入的ServerProperties类中定义了ErrorProperties类,ErrorProperties中又定义了默认的异常处理路径是/error;
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error;
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class })
@AutoConfigureBefore(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ ServerProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class })
public class ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration {
// 省略代码
}
以下是ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration中定义的几个较为重要的组件(Bean):
1.DefaultErrorAttributes
该Bean用于接收并传递异常相关的关键属性,如时间戳、请求状态、异常类名、异常信息、异常请求地址等。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes(this.serverProperties.getError().isIncludeException());
}
2.BasicErrorController
该Bean用于提取异常中的关键信息,并将其封装成错误信息页返回给请求调用者。(详细解析在这里)
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorController.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes,
ObjectProvider<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(),
errorViewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
3.ErrorPageCustomizer
该Bean用于向Spring注册ErrorPage(错误页抽象成的类),注册时将ErrorPage的URL路径设为了/error。
@Bean
public ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer(DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) {
return new ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, dispatcherServletPath);
}
4.其他Beans
除了上述三个Beans,还有PreserveErrorControllerTargetClassPostProcessor和
内置配置类DefaultErrorViewResolverConfiguration、WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration。
一、StandardHostValve
1)Tomcat采用Pipeline、Valve机制(相关内容可自行查询);
2)StandardHostValve是Tomcat中的一个默认基础Valve,负责处理Pipeline中流传过来的请求;
3)StandardHostValve会在Context中寻找合适的ErrorPage(未找到则使用默认的ErrorPage),并根据ErrorPage里的location转发请求;
// 以下是节选的部分与本文有关的逻辑处理代码,完整代码自行搜索查看
final class StandardHostValve extends ValveBase {
// valve的invoke()方法
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 获取到我们抛出的异常
Throwable t = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
if (response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
AtomicBoolean result = new AtomicBoolean(false);
response.getCoyoteResponse().action(ActionCode.IS_IO_ALLOWED, result);
if (result.get()) {
if (t != null) {
// 进入throwable()方法
throwable(request, response, t);
} else {
status(request, response);
}
}
}
}
// throwable()方法,用于处理request中的异常,产生异常对应的response
protected void throwable(Request request, Response response, Throwable throwable) {
Context context = request.getContext();
Throwable realError = throwable;
// 根据异常类名来查找对应的ErrorPage
// findErrorPage()最终执行了ErrorPageSupport类中的find()方法
// find()方法实际是去ErrorPageSupport维护的一个 Map<String, ErrorPage> 中查找ErrorPage
// 查询Map的key是throwable对象所代表类的完整类名
ErrorPage errorPage = context.findErrorPage(throwable);
if (errorPage != null) {
// 省略
} else {
// 找不到合适的ErrorPage,设置HttpStatus为500
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
// 将返回标记为Error
response.setError();
// 进入status()方法
status(request, response);
}
}
// status()方法,用于处理 HttpStatus
private void status(Request request, Response response) {
int statusCode = response.getStatus();
Context context = request.getContext();
// 根据HttpStatus来查找对应的ErrorPage
// 去ErrorPageSupport维护的另一个 Map<Integer, ErrorPage> 中查找ErrorPage
ErrorPage errorPage = context.findErrorPage(statusCode);
if (errorPage == null) {
// 找不到则使用默认的ErrorPage
errorPage = context.findErrorPage(0);
}
if (errorPage != null && response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
// 省略部分属性设置代码
// 进入custom()方法
// custom()方法根据errorPage里的location将请求发送到相应的Controller
// 这里会根据 /error 这个地址,将请求发送到BasicErrorController(当然中间还会经过DispatcherServlet)
if (custom(request, response, errorPage)) {
// 省略
}
}
}
// custom()方法,用于转发请求
private boolean custom(Request request, Response response, ErrorPage errorPage) {
try {
ServletContext servletContext =
request.getContext().getServletContext();
// errorPage.getLocation()值为 /error
RequestDispatcher rd =
servletContext.getRequestDispatcher(errorPage.getLocation());
if (response.isCommitted()) {
// 省略
} else {
// 转发请求
rd.forward(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
response.setSuspended(false);
}
return true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
// 省略
}
}
}
二、DispatcherServlet
1、DispatcherServlet 是 org.springframework.web.servlet 包下的一个 Java 类。
官方注释:
Central dispatcher for HTTP request handlers/controllers, e.g. for web UI controllers or HTTP-based remote service exporters.
Dispatches to registered handlers for processing a web request, providing convenient mapping and exception handling facilities.
个人翻译:
DispatcherServlet 是 SpringBoot 中 HTTP 请求的中央调度器,为 Web UI 或基于 HTTP 的远程发射器发送的请求提供服务。
其主要作用是向注册的可以处理 web 请求的 handlers 分发请求,并提供方便的映射、异常处理设施。
个人理解:
DispatcherServlet 类是 SpringBoot 的调度器,它负责组织和协调不同组件完成请求并返回响应结果。
DispatcherServlet 的主要任务是:①将请求发送至对应的 Controller/Handler、②请求结果处理及返回(正常及异常处理结果)。(本文只聚焦于异常处理部分)
2、StandardHostValve中转发的请求最终会由DispatcherServlet类中的doDispatch()方法来处理。
1)HandlerExecutionChain:处理链,包括Handler(Controller)和拦截器。
2)ModelAndView:用来存储请求处理返回的数据和视图。
3)HandlerAdapter:Handler适配器,主要用于用给定的Handler去处理Request。
// 以下是节选的部分与本文有关的逻辑处理代码,完整代码自行搜索查看
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// 当前请求
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
// 处理链(handler 和 拦截器)
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
try {
// 返回给用户的包装视图
ModelAndView mv = null;
try {
// 通过请求获取 handler
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
// 如果未找到 handler,报异常
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 根据 handler 找到 handlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 调用具体的 handler 处理请求,并返回 modelAndView
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
}
catch (Exception ex) { /* 省略 */ }
catch (Throwable err){ /* 省略 */ }
// 处理返回结果(异常处理、页面渲染、拦截器的 afterCompletion 触发等)
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) { /* 省略 */ }
catch (Throwable err){ /* 省略 */ }
finally { /* 省略 */ }
}
}
4)getHandler()方法会根据request中的请求地址/error获取到ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration注册的HandlerBasicErrorController。
三、BasicErrorController
BasicErrorController是SpringBoot中自带的基础全局错误处理器(Handler、Controller)。
1、请求地址
三元写法,若配置文件中配置了server.error.path,则使用此异常处理地址;若未配置则使用配置的error.path,
若error.path也未配置,则使用/error。
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
2、处理规则
根据@RequestMapping注解中的produces参数来匹配errorHtml()或error();
浏览器发出的请求header中Content-Type默认为text/html,postman中Content-Type默认为application/json;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections
.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
// 获取http请求状态
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
// 状态为204返回No Content
if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(status);
}
// 组装 timestamp、status、error、message、path
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
}
getErrorAttributes()方法的最终实现如下:
public class DefaultErrorAttributes implements ErrorAttributes, HandlerExceptionResolver, Ordered {
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<>();
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
addStatus(errorAttributes, webRequest);
addErrorDetails(errorAttributes, webRequest, includeStackTrace);
addPath(errorAttributes, webRequest);
return errorAttributes;
}
}
四、总结
1、刚开始这个主题时感觉根本无从下手,然后开始baidu、google,先找到BasicErrorController类,然后从它出发开始摸索。
2、要找清楚最终返回的五个属性是在哪段代码生成的,代码是怎么运行到BasicErrorController的error()方法的,http状态是在哪段代码中确定的等等。
3、一个比较好的方法是debug + 堆栈,可以从栈中找到代码运行过的轨迹,然后挨个去读源码。
4、个人觉得读源码最大的问题是不知道这个类是干啥的,这个时候baidu + google一波,再看类上的注释,大致就清楚了。